Recurrent Patella Dislocation
Understanding Recurrent Patella Dislocation
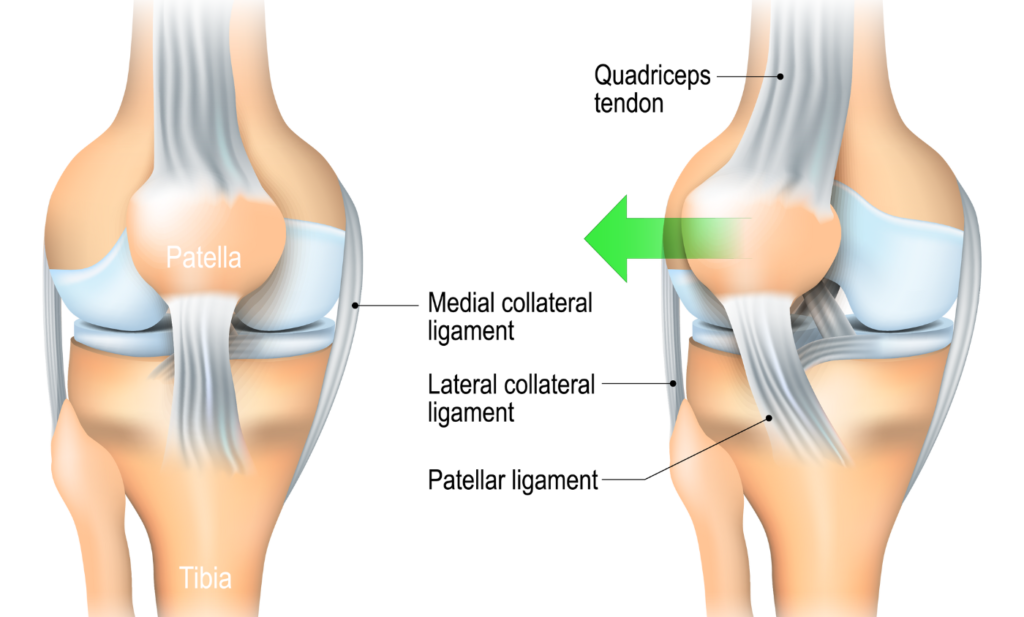
When your kneecap unexpectedly moves sideways out of its groove at the knee joint, that’s called a patella dislocation. It happens due to force, like a fall or a sudden twist. Dr. Vishal Mandlewala explains that even though it’s painful and makes walking difficult, fixing it is usually straightforward.
What is Patella (Kneecap ) Dislocation?
Your kneecap normally moves up and down in a groove at the knee joint. But during a dislocation, it’s forced out of this groove, making it hard to move the knee and tearing ligaments. Most dislocations happen when the kneecap is pushed sideways, usually from an accident or sudden movement.
What are the Causes of Recurrent Patella Dislocation?
Certain inherited traits:
✓ Knee cap that is seated too high in the groove
✓ Shallow trochlear groove
✓ Tight lateral ligaments
✓ Valgus leg alignment (knock-kneed legs)
✓ Trauma (twisting, bending, etc.)
✓ Athletes, dancers, teenagers, and people with loose joints are more at risk
✓ Skeletal immaturity
✓ Each dislocation causes stretching of soft tissues and increases the chances of recurrence
What are the Symptoms of Recurrent Patella Dislocation?
You might hear a pop, feel intense pain, and see swelling or bruising. It can be hard to walk, and the kneecap might look out of place, giving feeling kneecap may dislocate again.
Can you walk with a dislocated patella?
No. The knee will either be locked and unable to straighten or bend, or it will catch and pop when you try to bend it. The joint will be unstable and buckle when you try to bear weight on it. It will also be painful to move it. If you can walk, you may only have a patella subluxation.
If your dislocated patella pops back into place, you may be able to walk afterward. But the knee will still be swollen and painful from the trauma. You shouldn’t try to walk if it’s too painful.
How to diagnosed Recurrent Patella Dislocation?
The dislocation of the patella can be diagnosed with physical examination by Dr. Vishal Mandlewala at Renison Knee and Shoulder Clinic while you are sitting, lying down (supine, prone, and on your side), standing and walking. Dr. Vishal Mandlewala may order X-ray and CT scan to get a clear picture of the location of injury. You might also be advised to get an MRI done to assess the cartilage.
What is the Treating of recurrent Patella Dislocation?
Recurrent patella dislocation can be treated by non-surgical or surgical methods based on the severity of the condition.
Non-surgical treatment
Dr. Vishal Mandlewala will recommend conservative treatment if your knee cap has dislocated only once or twice.
The immediate aim of treatment will be to relieve pain with medication and practice PRICE, which includes Protection of the injured joint, Rest, applying Ice at the injured site, Compression, and Elevation of the leg to control inflammation.
Dr. Vishal Mandlewala might recommend you a limited period of immobilization with long knee brace.
Following immobilization Dr. Vishal Mandlewala will suggest you for patella hinged knee brace along with Renison knee and Shoulder Clinic Physiotherapy Protocol to strengthen your muscles.
Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain and swelling.
Surgical treatment
Surgery is recommended when non-surgical treatment is found to be ineffective in relieving the symptoms of recurrent patella dislocation. All realignment procedures performed to treat the dislocation will first involve arthroscopy. Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses 2 or 3 small incisions to insert surgical instruments at the site of the problem. The injured surface is can be cleaned to remove any loosely attached fragments. Following this, Dr.Vishal Mandlewala will decide on a surgical approach depending on the factors causing the dislocation.
✓ MPFL Reconstruction: To reconstruct the torn medial patellofemoral ligament, small holes are drilled in the patella and femur, and a piece of hamstring tendon (tissue connecting muscle at the back of the thigh to the knee) is passed into the holes to replace the torn MPFL. The tendons are fitted into place with the help of screws and anchors.
✓ Tibial Tuberosity Osteotomy: In case of a high seated patella, your surgeon will surgically realign the patella to fit into the groove of the thigh bone. This is done by moving the tibial tuberosity (part of the tibia). Screws are used to clasp the tuberosity and to hold it in position until complete healing.
✓ Trochleoplasty: is a rarely performed surgery, where the groove on the lower end of the femur is made deeper or reshaped. In this case, some bone is removed and the patella is held in place with sutures or nails, which dissolve over time.
✓ Your surgeon may also attempt to lengthen tight ligaments or tighten overstretched ligaments surrounding the kneecap.
Rehabilitation
As a postoperative management procedure, you will be advised to use crutches and wear a brace for the first few weeks. Once the bone has healed, you will be given physiotherapy and taught simple exercises to aid in normal functioning of the knee and to reduce swelling. You will be able to return to full activity in a few months.
Take Home Message:
Dr. Vishal Mandlewala at Renison Knee and Shoulder Clinic is experienced in treating Recurrent Patella Dislocation and can guide you through the process for a smooth recovery tailored to your needs.